Agricultural Adjuvants
Farmers today have to consider a variety of complex challenges. Apart from climatic changes such as drought and soil erosion, they have to meet the increasing demands and needs of the consumers.
“To remain competitive and profitable, they need to invest in both agricultural productivity and new technologies”
To support this agenda, Agricultural Adjuvants plays a very crucial role.
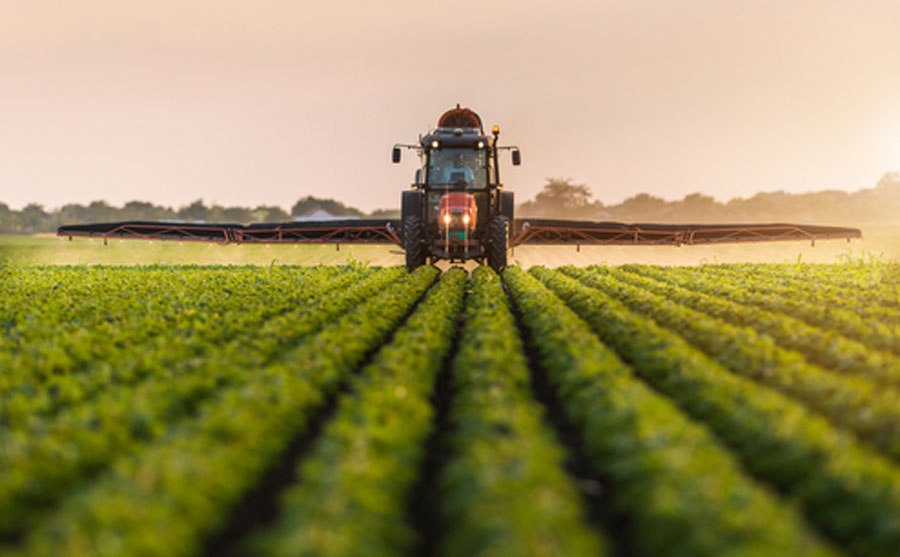
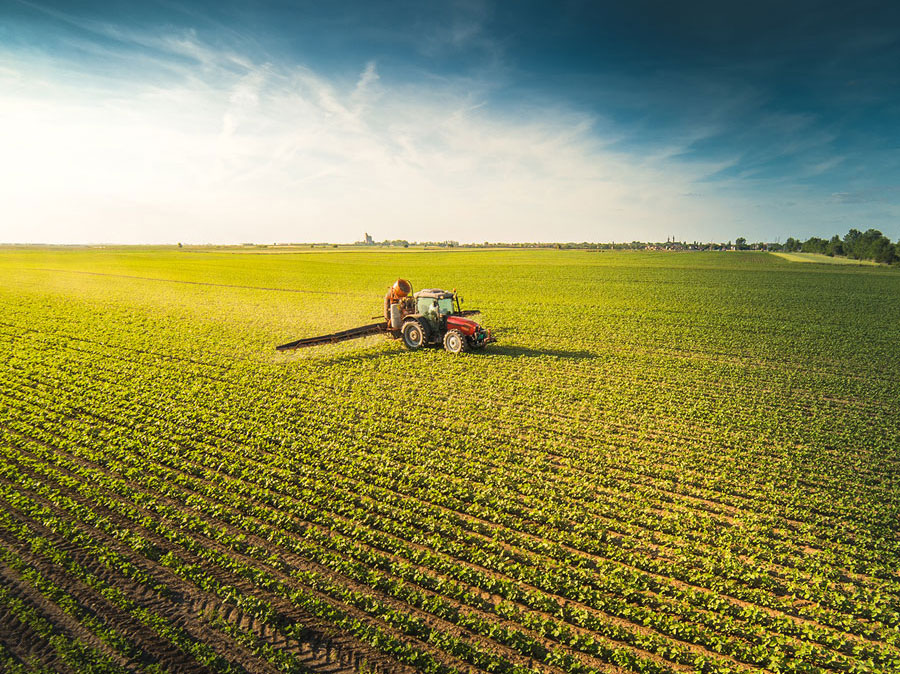


“Agricultural adjuvants” are used to enhance the effectiveness of pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, fungicides and other agents that control or eliminate unwanted pests. These additives may be included in a formulation with a pesticide or may be added separately to a tank.
Adjuvants are designed to perform specific functions involving the mixing and application of pesticides, such as buffering, dispersing, emulsifying, spreading, sticking, and wetting.
Adjuvants can also reduce evaporation, foaming, spray drift, and volatilization.
Type of Adjuvants
1. Activator Adjuvants
- Surfactants
- Non-ionic (incl. organosilicons)
- Ionic
- Amphoteric
- Oil Adjuvants (incl. crop oil concentrators)
- Ammonium (nitrogen) Fertilizer
2. Utility Adjuvants
- Wetting agent
- Dyes
- Thickening agents
- Drift control and foaming agent
- Water conditioner
- Depositions agents (Stickers)
- pH Buffers
- Defoaming and antifoaming agent
- Humectants
- UV absorbents