Paraffin Wax (or Petroleum Wax)
Paraffin Wax (or Petroleum Wax) is a soft colourless solid derived from petroleum, coal or shale oil that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between twenty and forty carbon atoms.
It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 °C (99 °F) and its boiling point is above 370 °C (698 °F).
It comes in three variants
1. Fully & Semi-Refined Paraffin Waxes – Fully and semi-refined Paraffin Waxes range from white to pale yellow colors and have a melting point in the range of 56-58 and 60-65 degrees centigrade, respectively. These types of Paraffin Waxes are commonly used in making candles and in the paper industry for making wax paper.
2. Granulated Paraffin Wax – Granulated Paraffin Wax is typically white-colored and has a melting point of roughly 58-62 degrees centigrade. This type of Paraffin Wax is used most in candle making, art applications, the tire industry, and for cosmetics purposes.


3. Liquid Paraffin – Liquid paraffin is also known as “white oil” or “mineral oil.” It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless. This form of Paraffin Wax is often used in hair care products and cosmetic grade cleansing creams because of its ability to soften and resist moisture loss. White oil is also common in pharmaceutical products, food, and textiles.
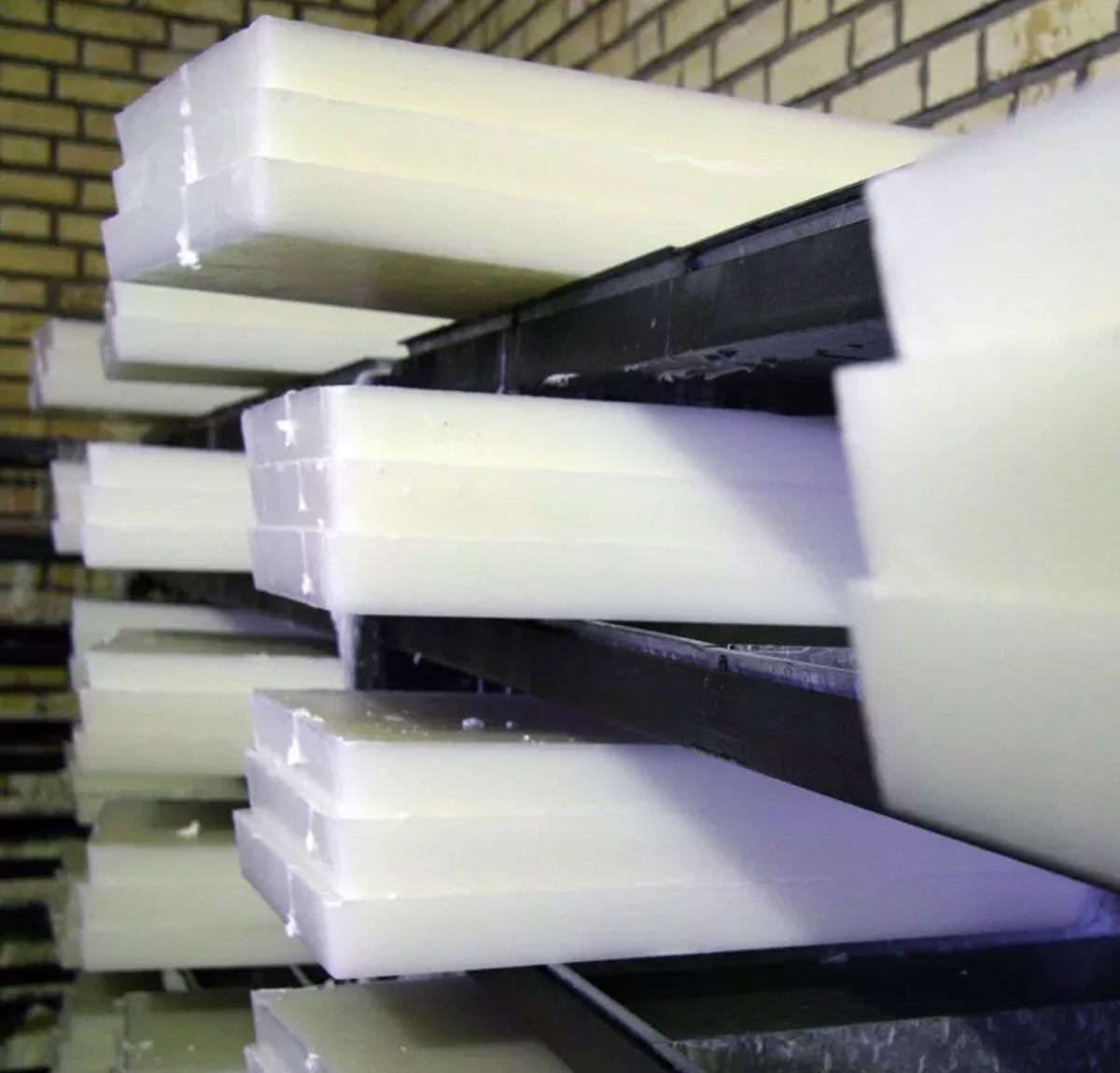
Available in both granule and slab form.
Grades available: 52, 54, 57, 60
Common applications include –
Lubrication, Electrical Insulation, Candles, Dyed Paraffin Wax, Crayons, Packaging, Petroleum Jelly, Grease, Thermostat and Distillation
Industrial Applications
In industrial applications, it is often useful to modify the crystal properties of the Paraffin Wax, typically by adding to the existing carbon backbone chain. The modification is usually done with additives, micro crystalline wax, or forms of polyethylene.

Specialized Industries
Candles
The candle industry is one of the major sectors for the consumption of refined Paraffin Wax in the world; it is the preferred material for making candles. Moreover, despite the progressive diversification of wax applications, candle manufacture continues to be the destination of most Paraffin Wax produced throughout the world.
Barrier Coating
Petroleum-based waxes and wax blends can be applied to numerous surfaces to reduce unwanted penetration or interactions of numerous liquids (water, grease, etc) and gases (oxygen, etc.).
Dental Wax
Paraffin Waxes and wax blends are formulated to be premium modelling waxes for use in dentistry. The waxes are usually provided by speciality businesses that utilize paraffin and microcrystalline waxes with other materials to make a finished dental wax
Crayons
Paraffin Waxes serve as a pigment binder. They assist in the transfer of the pigment from the crayon to the desired substrate.
Cosmetics (General)
Petroleum waxes serve as safe base material, solvent or carrier to provide a moisture barrier, modify viscosity, or solidify formulations.
Floor Polishes
Petroleum-based waxes enhance the gloss and buff ability characteristics of polish or paste primarily for wood floors.
Insulating Wax
Paraffin Waxes are utilized in numerous electrical applications as a result of their insulating capabilities.
Leather Treating
Crude scale and Paraffin Waxes are employed to soften and impart water repellent to leather goods.
PVC Lubricant
Paraffin Waxes provide external lubrication during the extrusion of PVC.
Rubber
Paraffin Wax is used as an additive in producing tyres, insulating them from ozone and avoiding cracks occurring in them.
Physiotherapy
Low melt paraffin and crude scale waxes are used in physiotherapy to provide heat to an injured area. Waxes permit a greater release of heat for a longer period than water which completely surrounds the part being treated and the patient does not need to remain in a fixed position.
Surface protection, paints and varnishes
Paraffin Waxes are used as additives in the production of printing inks and varnishes to improve the resistance of the products to friction or scratching or to achieve a certain appearance and to act as a barrier to moisture. It is also used as a ligand material for enamels, lubricating agents, corrosion protection, etc.
Petroleum-based waxes enhance the gloss and buff characteristics of polish or paste.
Some additional applications
- Bicycle/ Motorcycle chain lubrication
- Coatings for waxed paper or waxed cotton
- Solid propellant for hybrid rocket motors
- Antiozonant agents: Blends of paraffin and micro waxes are used in rubber compounds to prevent cracking of the rubber; the admixture of wax migrates to the surface of the product and forms a protective layer. The layer can also act as a release agent, helping the product separate from its mould.
- Moisturiser in toiletries and cosmetics such as Vaseline.
- Prevents oxidation on the surface of polished steel and iron.
- Phase change material for thermal energy storage